The emergence of server virtualization technology has provided business with a flexibility to scale the resources for turnkey solutions, optimized use of system capacity, and system performance monitoring. Today’s scope of business processes makes it impractical to monitor the resource load manually. Therefore, automatic balancing tools are used to ensure efficient operation of highly loaded infrastructures.
Why load balancing is needed
Load balancing is needed:
- to optimize the capacity utilization;
- to prevent overload of one or several resources;
- to ensure availability of services and applications launched, and to improve their performance;
- to decrease server response time;
- to reduce administrator’s efforts for system maintenance.
Failure to monitor load level as well as unrestricted utilization of resources at full capacity will have impact on the quality of services: increased response time or even unavailability of services and applications may occur.
Load balancing service in VMmanager
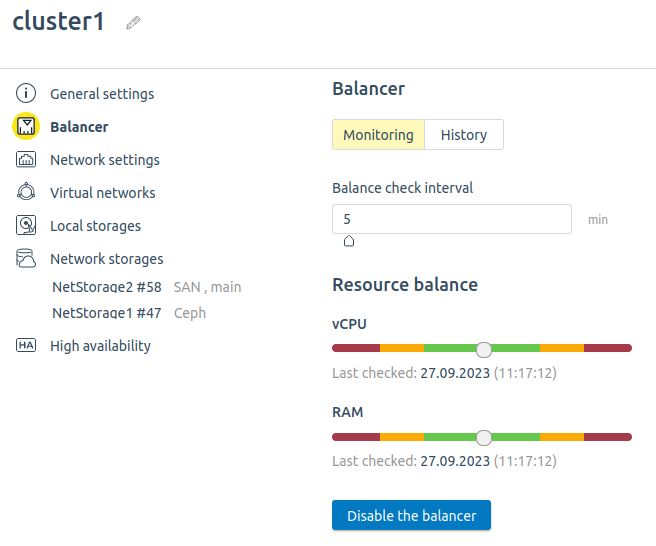
VMmanager server virtualization platform is capable of automatic load distribution and highly available environment. The Balancer has been developed for companies with highly loaded infrastructure, whose performance underpins positive user experience and efficiency of business processes.
The Balancer monitors load level of cluster nodes and redistributes virtual machines (VM) between nodes to balance the load. This allows for optimal utilization of available resources as well as working time of employees.
Key advantages:
- The Balancer is available out of the box with a single click activation.
- Administrator can set up check interval and load thresholds for CPU and RAM.
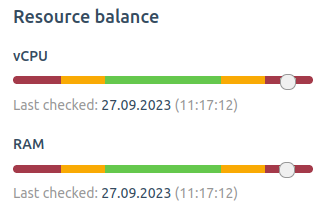
- The service built-in balance indicator allows to estimate node load visually.
- The Balancer migrates virtual machines between nodes without interruption in their operation, whereby all processes launched on virtual machines remain available.
The Balancer settings are configured by administrator, which allows to set up different parameters for each cluster. Whereas the service applies to all virtual machines in a cluster, you may use settings to select VMs, to which the Balancer will not be applied.
The logic of load balancing in VMmanager
The Balancer operation consists of the following iterations:
- collecting statistics;
- analyzing the obtained data and compiling lists of virtual machines for further migration;
- migration.
Let us have a closer look at each stage.
At the stage of statistics collecting, the Balancer has to understand what is happening with a node. In order to do so, it requires information about CPU average load, as well as RAM utilization. The service addresses the node at intervals prior configured by administrator in the settings. For example, if the parameter is set to 10 minutes, the Balancer will collect statistics for the last 10 minutes.
During the second stage – when the statistics have been collected – the service automatically divides the nodes into two lists. The first list includes the most loaded nodes; the second list includes the least loaded nodes. By default, virtual machines require migration to another node when the current node load reaches 70%. This parameter can also be configured to a higher or lower value in the settings. The Balancer automatically omits nodes that are under maintenance.
The third stage is migration. The Balancer migrates VM between nodes using a live migration mechanism, which keeps all virtual machines available throughout the whole process.
Once the migration is complete the service will repeat the procedure at a configured interval. History log shows all migrations that have been implemented.
Are there any restrictions?
Active Balancer does not ensure that all virtual machines are migrated to another node. The are several reasons for this. The most common are:
- On average it takes about one minute to check nodes in a cluster. This time is sufficient to analyze all virtual machines. But if there are too many nodes, this time may be insufficient for the Balancer to check them. In this case the report will be based on the data collected during one minute. Unchecked virtual machines will be registered in log files.
- If ISO image is mounted to VM, migration of another node to this VM is also not possible.
- If a VM has been migrated to another node during the last five iterations, the system will automatically exclude it from the candidates for migration.
- If a VM is turned off, it will also remain at its current node.
How to distribute load efficiently in VMmanager
In order to make load balancing service useful for optimized resource utilization rather than complicating things for administrator, it is recommended to comply with certain conditions:
- Do not fix on the default settings, but rather proceed from your needs. For example if a cluster is unbalanced, it is recommended that administrator reduce check interval to balance it. The same recommendation shall be followed if virtual machines are often created in and removed from a cluster.
- Reasonable threshold load values shall be configured. A node shall not be deemed overloaded at 50% load. In case the system indicates that load is reaching 100%, not only the Balancer will be useless but it will also consume additional resources of the node that is already at its limit.
- Scale cluster using additional nodes if current nodes are fully loaded. In this case balancing service will also engage resources to check and to migrate. This will have a negative impact on the service response time.
Takeaways
Let us make a brief summary: load balancing services, such as the Balancer in VMmanager, help owners of highly loaded infrastructures utilize their capacities efficiently by increasing availability of the environment and saving labor efforts of support team.
If you are using VMmanager, you can enable the Balancer in cluster settings. Find out about configuring the service operation in the documentation.