Now VMmanager supports L3 iBGP-based networks, otherwise known as IP fabric.
IP fabric is one the network cluster configuration types in VMmanager allowing you to set up a cluster of virtual machines with public IP addresses on top of your organization’s private local network.
Advantages of IP fabric
- Significant reduction of service traffic,
- Saving IP addresses,
- Isolation of virtual machines,
- Independence of virtual machine IP addresses from the nodes.
Important notice: IP fabric is only available in a cluster with nodes running on CentOS 8.
Technical description
Key notions
iBGP — dynamic routing protocol. This protocol manages exchange of routes between the nodes and the network equipment.
Node — the server where virtual machines are deployed.
Core Gateway — the core of the network, the main router of the segment.
Bird — the software enabling the work of iBGP protocol on Linux nodes.
Route reflector (RR) — the device that accepts routes from nodes and transmits them to Core Gateway via iBGP protocol.
Features of IP fabric
- The hypervisor does not have a Linux bridge,
- Virtual machines are assigned IP addresses with the /32 mask,
- A separate virtual interface on the node is a default gateway for each virtual machine,
- The nodes function as routers,
- Exchange of iBGP routes between the node and the neighboring Route Reflector,
- Routes to virtual machines are updated nearly in real time via the iBGP protocol,
- Public IP addresses are placed on top of the private network infrastructure.
Operating principle of iBGP in VMmanager
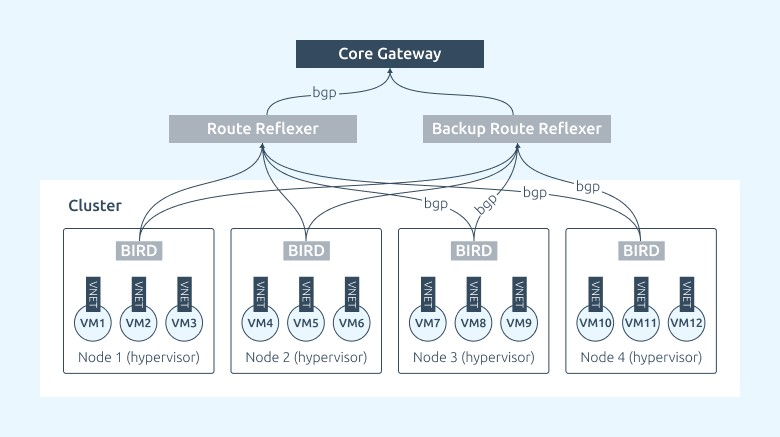
IP fabric operation logic
When a new virtual machine is created in VMmanager, the following processes are launched:
- Virtual machine deployment on the node,
- Configuration of routing on the node,
- Configuring the Bird service on the node,
- Bird announces the new route to the virtual machine via iBGP to the Route Reflector,
- The Route Reflector passes this route via iBGP further onto the Core Gateway,
- Core Gateway receives the information about the route to the new virtual machine and is able to process its traffic in both directions.
IP fabric allows migrating the virtual machine along with its IP address to a new node. In case of live migration, the virtual machine is unavailable for 5-10 seconds.
Important notice: Route Reflector does not participate in traffic routing, it is an "iBGP mediator" between the nodes and the Core Gateway. Thus, both physical servers and specialized equipment can be used as RRs.
How to try IP fabric
This configuration option is primarily for testing purposes and is not recommended for use in production. RRs are not used in this configuration: routes from the node are announced directly to the router.
What is required for testing
- A server managed by VMmanager.
- Two servers for the nodes with CentOS 8 installed. One node is sufficient if you are not planning to test migration.
- Access to the network equipment for configuring the iBGP session with a cluster.
- Details of autonomous iBGP system for VMmanager nodes and Core Gateway.
- IP pool for virtual machines
Configuration algorithm
- Install VMmanager on the server.
- In VMmanager, create a cluster with the IP fabric network type.
- Specify the details for communication with Core Gateway via iBGP.
- Specify the details for connection to the first node.
- Specify the details of the network and IP addresses for virtual machines.
- Connect the second node.
- Configure the iBGP sessions to each node on the Core Gateway.
- VMmanager is now ready!
