This article describes methods for diagnosing network issues. To follow the instructions in this article, connect to the target server via SSH. For more information about connecting via SSH, see Workstation setup.
The diagnostic procedure depends on the network configuration type:
- switching. The physical interface on the cluster node and the virtual machine (VM) interfaces are connected to the same bridge. There is no routing within the cluster node. For packets destined for a VM arriving on the physical interface, the cluster node's OS determines the target virtual interface using an ARP request;
-
routing. The VM virtual interfaces are connected to a bridge. Packet forwarding between the physical interface and the bridge is handled by routes in the cluster node's OS:
- a route to the subnet from which IP addresses are assigned to VMs;
- host routes to specific IP addresses.
The packet is then delivered to the virtual interface within the bridge.
- IP fabric. There is no bridge on the cluster node. Packet forwarding between the physical and virtual interfaces is handled by host routes to specific IP addresses in the cluster node's OS. The FRR service ensures route relevance.
For more details, see the Cluster network configurations article.
Toolkit
This section lists the utilities required for diagnosing VM network connectivity.
Linux
Diagnostic utilities:
- arping — to detect hosts on a computer network;
- bridge — to manage bridge interfaces;
- curl — to create network requests for different data protocols: FTP, FTPS, HTTP, HTTPS, TFTP etc.;
- dig — to check the DNS records of a domain;
- ip — to check and configure network interfaces;
- iperf3 — to measure the bandwidth of the network;
- mtr — to check the network connection;
- nc — to send and receive data via TCP and UDP;
- nmap — to explore network and perform security checks;
- ping — to check if the remote host is available;
- ss — to analyze the network connections of the system;
- tcpdump — to analyze network traffic;
- tracepath and traceroute — to display possible packet routes.
To get detailed information about the features, syntax and keys of the Linux utility, run the command:
sudo man <utility>If a required utility is missing from the server, install it:
sudo dnf install <utility_name>sudo apt install <utility_name>Windows
Diagnostic utilities:
- ipconfig — to manage network interfaces;
- netsh — to display or edit the network configuration;
- netstat — to display information about the system's UDP and TCP connections;
- nslookup — to run DNS queries;
- ping — to check if the remote host is available;
- route — to view, delete and add static routes to the system routing table;
- tracert — for network diagnostics.
Preliminary diagnostics
To rule out basic problems, perform preliminary diagnostics:
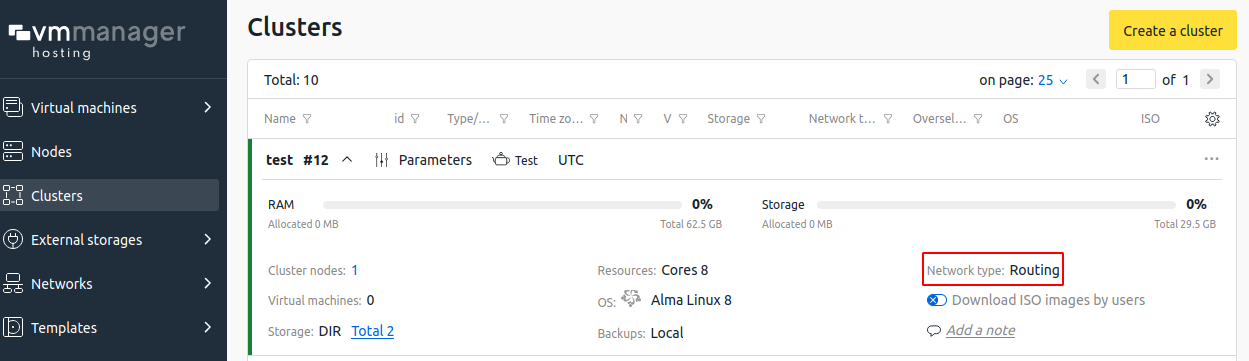
- Determine the network configuration type in the cluster. To do this, go to Clusters → select a cluster → see the Network Type field.
-
Check the cluster node's accessibility:
docker exec -it vm_box bash vmssh -p <SSH_port> <Node_IP_address>The node should be accessible via SSH from the platform server inside the vm_box container. If the connection fails, follow the recommendations in the article If the cluster node is unavailable.
- Make sure that the server configuration matches the selected type of network configuration.
- switching:
-
Check for a bridge:
ip address show -
Check the network interfaces connected to the bridge:
bridge link show
-
- routing:
-
Check for a bridge:
ip address show -
Check the network interfaces connected to the bridge:
bridge link show -
Check for routes:
to show IPv4 routesip route showto show IPv6 routesip -6 route show
-
- IP fabric:
-
Check for host routes:
to show IPv4 routesip route showto show IPv6 routesip -6 route show
-
- switching:
Bring the configuration into compliance with the selected network type. In complex cases (e.g., if a required bridge is missing), the most reliable method is to remove the node from the cluster, reinstall the OS on the server, and reconnect the node. If this is not possible (the node is already in production), correct the settings in the configuration files:
- /etc/sysconfig/networks-scripts for AlmaLinux;
- /etc/network/interfaces for Ubuntu, Astra Linux.
Diagnosing network problems on a node
- Identify the type of network problem. For example, the guest OS does not respond to ping, a specific TCP/UDP port is unavailable, etc. The choice of troubleshooting tools depends on your network hardware settings and ISP restrictions. For instance, if the ICMP protocol is completely blocked, the ping utility will be useless for diagnostics.
-
On the cluster node, run the tcpdump utility on the physical interface:
tcpdump -i <interface_name> -enn -vvv host <VM_IP_address> -
Send packets to the target VM depending on the identified problem type:
-
if checking via ICMP:
ping <VM_IP_address> -
if checking IPv4 TCP port availability:
nmap -Pn -sS <VM_IPv4_address> -p <TCP_port> -
if checking IPv4 UDP port availability:
nmap -Pn -sU <VM_IPv4_address> -p <UDP_port> -
if checking IPv6 TCP port availability:
nmap -6 -Pn -sS <VM_IPv6_address> -p <TCP_port> -
if checking IPv6 UDP port availability:
nmap -6 -Pn -sU <VM_IPv6_address> -p <UDP_port>
-
If tcpdump on the physical interface does not show sent packets, check for ARP requests (IPv4 traffic) or NDP requests (IPv6 traffic) to VMs:
tcpdump -i <interface_name> -enn -vvv arp | grep '<IPv4_IP_address>'tcpdump -i <interface_name> -enn -vvv icmp6 | grep '<IPv6_IP_address>' | grep -P 'advertisement|solicitaton'As a result, two options are possible:
- there are no ARP/NDP requests on the physical interface. This means that the problem is not related to the operation of the node. Consult your network engineer to solve the problem;
- there are ARP/NDP requests without responses on the physical interface. In this case, check that the requests are forwarded to the virtual interface of the VM:
-
Get the name of the virtual interface:
virsh domiflist <VM_libvirt-domain_ID_or_name> -
Check the queries with the commands:
ARPtcpdump -i <interface_name> -enn -vvv arp | grep '<IPv4_IP_address>'NDPtcpdump -i <interface_name> -enn -vvv icmp6 | grep '<IPv6_IP_address>' | grep -P 'advertisement|solicitaton'
If ARP/NDP requests are also displayed on the virtual interface without responses, further diagnostics is performed in the guest OS.
Diagnosing network problems in the guest operating system
The principles of diagnosing network problems in the guest OS are the same as on the node server. For diagnostics:
- Check IPv4 or IPv6 settings in the guest OS against those specified for the problematic VM in the platform. Run the commands:
- Linux:
-
to display the network interfaces:
ip address show -
to display the IPv4 routes list:
ip route show -
to display the IPv6 routes list:
ip -6 route show
-
- Windows:
-
to display the network interfaces list:
ipconfig /all -
to display the routes list:
route print
-
- Linux:
-
On the nodeserver, run the tcpdump utility on the virtual interface of the problem VM:
-
Get the name of the virtual interface:
virsh domiflist <VM_libvirt-domain_ID_or_name> -
Run the command:
tcpdump -i <interface_name> -enn -vvv
-
- Send ICMP (ping utility) or TCP/UDP (nmap utility) packets to an external address. The response options are as follows:
- the sent packets are not visible on the virtual interface of the problematic VM. In this case, the problem is most likely in the firewall settings in the guest OS;
- the sent packets are visible on the virtual interface of the problematic VM. In this case, run tcpdump on the physical interface of the node server. If packets are visible there as well, the problem is somewhere outside the node. Consult a network engineer to solve the problem;
- packets are lost between the virtual and physical interface on the node server. In this case, check again the network and firewall settings on the node.
 En
En
 Es
Es