VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a group of devices that appear to be on the same LAN despite their geographical distribution. They can be connected to different network switches. Devices located in different VLAN are not visible for each other even if they are connected to the same switch.
VLAN is a mechanism for creating a logical network topology regardless of its physical topology. VLANs are used for reducing broadcasting traffic in the network. It allows increasing security, particularly, as an ARP-spoofing protection tool.
VLAN types:
- port-based;
- MAC-based;
- protocol-based;
- authentication.
How it works
DCImanager supports port-based VLANs. Physical switch ports are grouped logically into VLAN. Port-based VLAN allows for better management, security, and configuration in comparison with other types.
DCImanager supports Trunk ports. Trunk ports are used to carry traffic that belongs to multiple VLANs between devices over the same port. Tags are Information about the VLAN that the frame belongs to. This feature requires that you have several switches. Two switches are connected only by two trunk ports that can carry traffic from any number of VLANs.
DCImanager can work with Primary and Isolated PVLAN.
Private VLAN (PVLAN) is a technology that allows isolating switch ports. Private VLAN divides VLAN (primary) into several sub-VLANs (secondary) and preserves the existing IP subnet and layer 3 configurations.
Primary VLAN includes the Promiscuous port. This is a switch port connected to devices of a higher level (a switch, router, etc.).
Secondary VLAN. Types of secondary VLAN ports:
- Isolated — any switch ports added into Isolated VLAN; they can be connected to Primary VLAN, but not to other Secondary VLAN and other hosts within the same Isolated VLAN.
- Community — any switch ports added into VLAN; the can be connected to Primary VLAN and each other, but not to Secondary VLAN.
Brocade ICX(Mult) allows working with PVLAN. For other switches, PVLAN support is specified in Supported devices.
DCImanager supports "Vlan per user" (VPU) configuration. VPU allows placing every server (a group of servers) into a separate broadcast domain. Every server (a group of servers) is assigned a separate VLAN, and the IRB-interface with this VLAN is created on the router. IRB interface is a logical Layer 3 which is used as the default router for VLAN.
Example configuration:
- The VLAN and network with prefix 31 (two IP addresses) are reserved for VLAN. One IP address is for the router, the other - for the server. The networks of alias addresses may be different.
- Configure the IRB-interface with the IP address from the server network and its VLAN on the router.
- Configure the DHCP-relay on DCImanager IP address. You can find the configuration commands in the list of networks for the VLAN.
- Alias addresses /32 are routed to the primary IP as follows: route x.x.x.16/32 next-hop x.x.x.97.
- Alias addresses are set using the dynamic routing protocol. DCImanager uses Bird. For more information please refer to the official website.
To use the VPU functions you need to install the corresponding module (starting from version 5.155) or enable the option Enable VPU in Settings → Global settings (before version 5.155).
VLAN modules
DCImanager uses the following modules to improve VLAN functions::
1. "VPU (Vlan Per User)" (starting from version 5.155). Allows placing each server (a group of servers) into a separate broadcast domain.
2. "User VLAN". Allows users to place their servers in VLAN allowed by the administrator.
To set up and configure the module, navigate to Integration → Modules
VLAN management
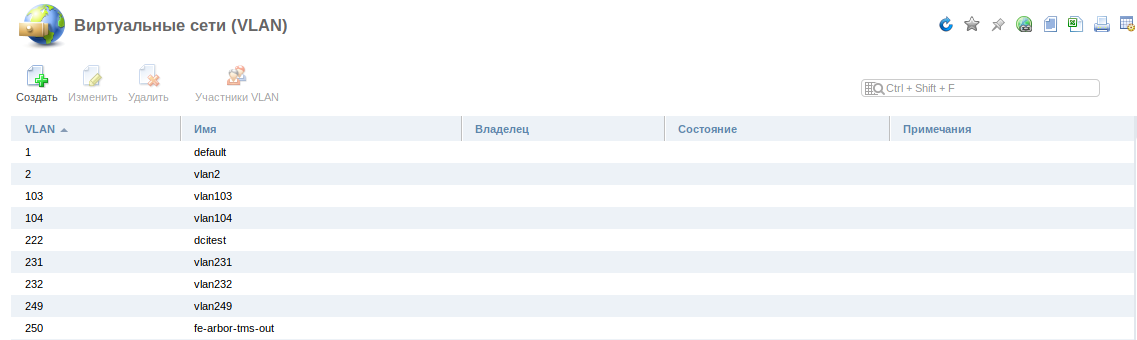
Navigate to Main→ VLAN
View a list of virtual networks.
- The VLANs that were created manually;
- The VLANs that were found automatically.
Adding a virtual network into DCImanager manually
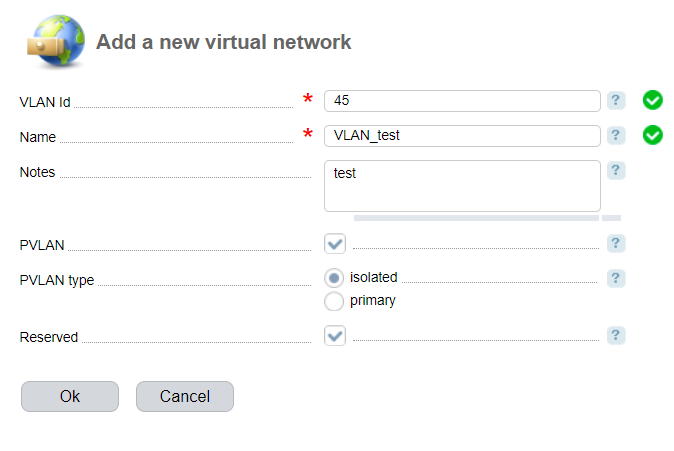
Navigate to Main → VLAN → click Add.
- VLAN Id — the virtual network unique identifier;
- Name — the name of the virtual network which is used when configuring network equipment;
- Owner — a user who can use the VLAN on servers;
- Notes - additional information that you can see in the list of VLANs → the "Notes" column;
- PVLAN — select the checkbox to enable PVLAN;
- PVLAN type — select a type of the virtual network.
- isolated — secondary VLAN of the isolated type;
- primary — primary VLAN;
- Reserved — select the checkbox not to specify the VLAN settings on the router.
Adding VLAN automatically
During the configuration process, the administrator assigns the required VLANs to the switch ports. DCImanager will be synchronized with the VLAN configured on the devices: the system will set VLANs found on the ports, marks the trunk ports and their trunk members.
Adding a switch port into VLAN
Navigate to Equipment → Switches → Ports → Edit.
The port settings associated with the VLAN configuration:
- Trunk mode — select the checkbox to activate the Trunk mode for the port. Enter the following parameters:
- Native VLAN — the untagged VLAN;
- Trunk members — VLANs that can pass the traffic through the port;
- UpLink — select the checkbox, if this port is connected to a switch/router of a higher level (switch, router, etc.). This port won't be displayed in the list of ports when connecting a new device. The system won't search for new servers on this port. Administrators cannot perform any operations (change VLAN, speed, or mode).
If you need to add a large number of VLANs, we recommend that you perform this operation directly on the switch. DCImanager will apply the changes automatically.
Configuring IP addresses in VLAN
Log in to IPmanager and create a group of IP address for the VLAN. Specify the group in the user permissions form for the corresponding subnet in IPmanager. In the Block of IP addresses field specify the newly created group of addresses or every server that will work in the VLAN.
Navigate to Settings → Global settings → Policy and select a standard type of IP addresses. All new servers will be configured with the selected type if another value is not specified in the Pool of IP addresses field.
 En
En
 Es
Es